Eco-friendly packaging refers to sustainable, biodegradable, compostable, recyclable, or reusable materials. These packaging solutions are designed to minimize environmental impact throughout their life cycle—from production to disposal.
The importance of eco-friendly packaging lies in its ability to reduce waste, conserve natural resources, and lower carbon emissions associated with traditional packaging methods.
As businesses shift towards sustainability, adopting eco-friendly packaging fulfills corporate social responsibility and meets the growing consumer demand for environmentally conscious products.
According to a study by McKinsey & Company, 67% of consumers consider sustainability when making purchasing decisions, highlighting the need for brands to align their practices with consumer values.
Environmental Impact of Traditional Packaging
Traditional packaging materials, particularly plastics, have severe environmental consequences. Plastic waste contributes significantly to pollution in oceans and landfills, taking hundreds of years to decompose.
The World Economic Forum estimates that if current trends continue, there could be more plastic than fish in the oceans by 2025.
Moreover, traditional packaging production processes often involve high energy consumption and greenhouse gas emissions. For instance, producing plastic involves extracting and processing fossil fuels into usable materials, contributing to climate change. In contrast, eco-friendly alternatives aim to mitigate these impacts by utilizing renewable resources and reducing waste.
Types of Eco-Friendly Packaging Materials
The following is an overview of eco-friendly packaging materials, detailing biodegradable options, compostable materials, recycled and recyclable packaging, and plant-based solutions. Each type plays a vital role in reducing environmental impact and promoting sustainability.
Overview of Eco-Friendly Packaging Materials
Eco-friendly packaging encompasses a range of materials designed to minimize environmental harm. These materials can be categorized into several types:
- Biodegradable Packaging: Made from natural substances that break down into harmless environmental byproducts.
- Compostable Packaging: Similar to biodegradable but specifically designed to decompose in composting conditions, enriching the soil.
- Recycled and Recyclable Packaging: Utilizes post-consumer materials or can be processed again after use, reducing the need for virgin resources.
- Plant-Based Packaging Solutions: Derived from renewable plant sources, these materials offer sustainable alternatives to traditional plastics.
Biodegradable Options
Biodegradable packaging is crafted from natural materials such as cornstarch, sugarcane, and bamboo. These substances can decompose into non-toxic components when exposed to natural environmental conditions. For instance:
- Corn Starch: Often used for making bags and containers that break down within months.
- Sugarcane: Used in producing bio-based plastics that are more sustainable than conventional petroleum-based plastics.
Biodegradable packaging significantly reduces landfill waste as it breaks down faster than traditional plastics, which can take centuries to decompose.
Compostable Materials
Compostable packaging is designed to break down in composting environments, transforming into nutrient-rich compost. Common compostable materials include:
- PLA (Polylactic Acid): A bioplastic derived from corn starch that decomposes under industrial composting conditions.
- Paper Products: These are made from recycled paper or sustainably sourced wood pulp and can also be composted after use.
Compostable options are particularly beneficial in food service settings where they can enhance soil health while minimizing waste.
Recycled and Recyclable Packaging
Recycled packaging utilizes materials that have been processed from post-consumer waste. Commonly used recyclable materials include:
- Kraft Paper: Known for its durability and recyclability, it can be repulped and reused multiple times.
- Aluminum: Highly recyclable with a closed-loop process that allows it to be reused indefinitely without losing quality.
Recyclable packaging helps conserve resources by reducing the demand for new raw materials and minimizing landfill contributions.
Plant-Based Packaging Solutions
Plant-based packaging solutions are made from renewable resources such as:
- Bioplastics: These are derived from plants like sugarcane or potatoes and offer a more sustainable alternative to traditional plastics.
- Mushroom Packaging: Created using mycelium (mushrooms’ root structure), this innovative material is fully compostable and can replace Styrofoam in protective packaging applications.
Plant-based solutions reduce reliance on fossil fuels and contribute to a circular economy by utilizing renewable resources.
Benefits of Eco-Friendly Packaging
Eco-friendly packaging offers many advantages that extend beyond environmental conservation. This section highlights four key benefits: reduced carbon footprint, minimized waste, conservation of natural resources, and improved brand image.
Reduced Carbon Footprint
One of the most significant benefits of eco-friendly packaging is its ability to lower carbon emissions throughout the supply chain. Traditional packaging materials, particularly plastics, are energy-intensive and often involve fossil fuels. In contrast, eco-friendly alternatives require less energy and generate fewer greenhouse gases.
Statistical Insight: According to a report by the Ellen MacArthur Foundation, switching to biodegradable and compostable materials can reduce carbon emissions by up to 70% compared to conventional plastic packaging.
Companies can reduce their carbon footprint by choosing eco-friendly options and contribute to global efforts in combating climate change.
Minimized Waste
Eco-friendly packaging solutions are designed to minimize waste at every stage of their lifecycle. This includes:
- Biodegradable and Compostable Materials: These materials break down naturally, reducing the volume of waste sent to landfills.
- Recyclable Packaging: Encouraging consumers to recycle helps divert materials from landfills and promotes a circular economy.
- Minimalist Design: Many eco-friendly packages are designed with minimal material usage, reducing waste.
Statistical Insight: The U.S. Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) reported that recycling and composting prevented the release of approximately 186 million metric tons of carbon dioxide equivalent into the air in 2018.
By adopting eco-friendly packaging strategies, businesses can significantly contribute to waste reduction efforts.
Conservation of Natural Resources
Eco-friendly packaging plays a crucial role in conserving natural resources. Companies can reduce their dependence on virgin materials using recycled or renewable resources. This has several benefits:
- Reduced Deforestation: Using recycled paper products decreases the need for new wood pulp, helping preserve forests.
- Sustainable Sourcing: Plant-based materials are often sourced from renewable crops that can be replenished annually.
- Water Conservation: Many eco-friendly materials require less water during production than traditional packaging.
By conserving natural resources, businesses protect ecosystems and ensure that these resources remain available for future generations.
Improved Brand Image
Consumers increasingly prefer brands that prioritize sustainability in today’s environmentally conscious market. Adopting eco-friendly packaging can enhance a company’s brand image in several ways:
- Consumer Trust: Brands that demonstrate a commitment to sustainability often gain higher consumer trust and loyalty.
- Competitive Advantage: Companies using eco-friendly packaging can differentiate themselves from competitors not prioritizing sustainability.
- Positive Public Relations: Sustainable practices can promote favorable media coverage and enhance a company’s reputation.
- Statistical Insight: A Nielsen survey found that 66% of global consumers are willing to pay more for sustainable brands.
Eco-Friendly Packaging Design Principles
Understanding and applying eco-friendly packaging design principles is crucial for businesses aiming to reduce their environmental footprint. This section outlines four key principles: minimalism and reduced material use, reusability and multi-functionality, easy recyclability or compostability, and non-toxic inks and adhesives.

Minimalism and Reduced Material Use
Minimalism in packaging design emphasizes using fewer materials without compromising product protection. This principle involves:
- Lightweight Packaging: Reducing the weight of packaging materials decreases transportation emissions and costs. For example, companies like Apple have adopted minimalist designs that save materials and enhance aesthetic appeal.
- Efficient Shapes: Designing packaging optimally fits the product reduces excess material usage. Innovative shapes can lead to more efficient shipping and storage, lowering environmental impact.
Reusability and Multi-Functionality
Reusable packaging is designed to be used multiple times, promoting a circular economy. Key aspects include:
- Refillable Containers: Brands like The Body Shop offer refillable options that encourage customers to return for refills, reducing single-use waste.
- Multi-Purpose Designs: Packaging that serves more than one function can extend its lifecycle. For instance, a box that can be repurposed as storage after its initial use adds value for consumers.
Easy Recyclability or Compostability
Designing packaging with recyclability or compostability in mind is essential for reducing landfill contributions. This involves:
- Material Selection: Using single-material solutions enhances recyclability. For example, mono-material packaging made entirely from paper or cardboard simplifies recycling.
- Clear Labeling: Providing clear instructions on recycling or compost packaging helps consumers dispose of it correctly. Brands should avoid mixed materials that complicate recycling efforts.
By focusing on recyclable or compostable materials, businesses can contribute to a reduction in waste while promoting responsible consumer behavior.
Non-Toxic Inks and Adhesives
The use of non-toxic inks and adhesives is critical in eco-friendly packaging design. This principle includes:
- Soy-Based Inks: These inks are less environmentally harmful than traditional petroleum-based inks. They are biodegradable and reduce the overall chemical footprint of the packaging.
- Safe Adhesives: Utilizing adhesives that do not contain harmful chemicals ensures the packaging is safe for consumers and the environment.
Food and Beverage: Focus on Eco-Friendly Food Packaging
The food and beverage industry is at the forefront of the eco-friendly packaging movement. The global market for eco-friendly food packaging was valued at approximately $197 billion in 2023 and is projected to reach $319.4 billion by 2030, growing at a CAGR of 7.1%. Key trends include:
- Biodegradable Materials: Many companies are shifting towards biodegradable options from plant-based materials like corn starch and sugarcane, which decompose naturally without leaving harmful residues.
- Recyclable Packaging: Brands are increasingly utilizing recycled materials to minimize waste. For example, Amcor launched a recycled food packaging solution that reduces carbon footprints significantly.
- Minimalist Design: Simplifying packaging reduces material use and appeals to consumer preferences for sustainable practices.

Eco-Friendly Coffee Packaging Trends
The coffee industry is also adapting to eco-friendly practices. With an increasing number of consumers expressing concern about environmental issues, brands are exploring sustainable packaging options:
- Compostable Coffee Bags: Many companies now use compostable bags made from renewable resources that break down in composting environments.
- Reusable Containers: Some brands have introduced refillable coffee containers that encourage customers to return for refills, reducing single-use waste.
- Innovative Materials: There is a growing trend towards using materials derived from agricultural waste or bioplastics to package coffee products sustainably.
Cosmetics and Personal Care
The cosmetics industry is witnessing a shift towards sustainable packaging as brands respond to consumer demand for eco-friendly products:
- Recyclable Containers: Many cosmetic brands are adopting recyclable glass or aluminum containers that can be reused or repurposed.
- Refill Programs: Companies like Lush have implemented refill stations for their products, allowing customers to bring in old containers for refills.
- Plant-Based Inks: Using non-toxic inks derived from plants enhances the sustainability of cosmetic packaging while ensuring consumer safety.
E-Commerce and Shipping
The rise of e-commerce has prompted significant changes in shipping practices, leading to an increased focus on eco-friendly packaging:
- Sustainable Shipping Materials: Companies opt for biodegradable packing peanuts, recycled cardboard boxes, and paper tape instead of plastic alternatives.
- Minimal Packaging Solutions: Brands are adopting minimalist packaging designs that reduce waste while ensuring product safety during transit.
- Consumer Education: Many e-commerce platforms are educating consumers on how to recycle or compost their packaging materials effectively.
Electronics and Technology
The electronics sector is also making strides toward sustainability by implementing eco-friendly packaging solutions:
- Recycled Materials: Tech companies increasingly use recycled plastics and cardboard for product packaging.
- Innovative Designs: Brands like Apple have adopted minimalist designs that reduce material use and enhance consumers’ unboxing experience.
- Sustainable Practices: Companies focus on reducing their overall carbon footprint through sustainable sourcing of materials and responsible product disposal options.
Innovative Eco-Friendly Packaging Solutions
As the demand for sustainable packaging grows, several innovative materials have emerged. This section discusses four key solutions: edible packaging, dissolvable packaging, mushroom-based packaging, and seaweed and algae-derived materials. Each of these options offers environmentally friendly alternatives to traditional packaging.

Edible Packaging
Edible packaging is made from food-grade materials that can be safely consumed along with their products. This innovative approach not only reduces waste but also enhances the consumer experience.
- Examples: Companies like MonoSol have developed water-soluble films for various food products, including coffee and pasta. When placed in hot water, these films dissolve completely, leaving no waste.
- Benefits: Edible packaging can help significantly reduce plastic waste, eliminating the need for separate packaging materials that often end up in landfills.
Dissolvable Packaging
Dissolvable packaging represents a new frontier in sustainable materials. Made from biodegradable polymers like Polyvinyl Alcohol (PVA), it dissolves in water, leaving no harmful residues.
- Applications: Dissolvable plastics are suitable for lightweight products such as compost bags or magazine wraps. When disposed of properly, they can dissolve within minutes in hot water.
- Environmental Impact: This type of packaging helps mitigate plastic pollution by providing a solution that breaks down quickly and safely, reducing the burden on recycling facilities and landfills.
Mushroom-Based Packaging
Mushroom-based packaging is made from mycelium (mushrooms’ root structure) combined with agricultural waste like corn husks. This material is 100% biodegradable and compostable.
- Production Process: Mycelium grows around clean agricultural waste, binding it into a solid shape. Once dried, this material is durable enough to protect fragile products during shipping.
- Sustainability: Mushroom packaging reduces plastic use and enriches soil when composted, contributing to a circular economy by returning nutrients to the earth.
Seaweed and Algae-Derived Materials
Due to their rapid growth rates and minimal environmental impact, seaweed, and algae are increasingly being explored as sustainable alternatives for packaging materials.
- Innovative Uses: Seaweed-based films can be used for wrapping food products or creating biodegradable containers. They decompose naturally in marine environments without harming aquatic life.
- Market Potential: The market for seaweed-derived materials is expanding as consumer awareness of ocean health grows. These materials reduce reliance on fossil fuels and promote sustainable harvesting practices.
Implementing Eco-Friendly Packaging in Business
Transitioning to eco-friendly packaging involves a systematic approach that includes assessing current practices, selecting sustainable materials, redesigning packaging, and educating consumers. This section discusses these key steps in detail.
Conducting a Packaging Audit
The first step in implementing eco-friendly packaging is conducting a thorough packaging audit. This involves evaluating the current packaging materials and processes to identify areas for improvement.
- Assessment Criteria: Consider material types, waste generation, recyclability, and sourcing practices. This helps identify which materials harm the environment and which can be replaced with more sustainable options.
- Data Collection: Gather data on the volume of packaging used, costs associated with current materials, and waste disposal methods. This information will guide decisions on which eco-friendly alternatives to adopt.
- Benchmarking: Compare your findings against industry standards or competitors to understand where your business stands regarding sustainability.
Selecting Appropriate Eco-Friendly Packaging Materials
Once the audit is complete, the next step is to choose suitable eco-friendly packaging materials that align with your business needs.
- Material Options: Look for materials that are recyclable, biodegradable, or made from renewable resources. Options include recycled cardboard, bioplastics derived from plants like corn or sugarcane, and compostable materials like PLA (polylactic acid) .
- Supplier Collaboration: Partner with suppliers who prioritize sustainability and offer eco-friendly options. Engaging in discussions about your commitment to sustainable practices can encourage suppliers to support your initiatives.
- Performance Evaluation: Ensure the selected materials meet performance requirements without compromising product protection or customer experience.
Redesigning Packaging for Sustainability
Redesigning packaging is crucial for maximizing sustainability while maintaining functionality and aesthetics.
- Minimalist Design: Adopt minimalist designs that reduce material usage without sacrificing product protection. This not only lowers costs but also appeals to environmentally conscious consumers.
- Multi-Functional Packaging: Create packaging that serves multiple purposes or can be reused by consumers. For example, designing boxes that can be repurposed as storage solutions encourages reuse.
- Easy Recycling: Ensure the packaging is designed for easy recycling or composting. Use single-material solutions widely accepted in recycling programs and clearly label them to guide consumers on proper disposal methods.
Educating Consumers About Proper Disposal
Educating consumers on properly disposing of eco-friendly packaging is essential for maximizing its environmental benefits.
- Clear Instructions: Provide clear labeling on packaging regarding recycling or composting instructions. This empowers consumers to make informed choices about disposal.
- Awareness Campaigns: Launch campaigns that educate consumers about the importance of responsible disposal and how it contributes to sustainability efforts. Highlight the environmental impact of improper disposal methods.
- Incentives for Recycling: Consider offering incentives for customers who return used packaging or participate in recycling programs. This can foster loyalty while encouraging sustainable practices.
Challenges in Adopting Eco-Friendly Packaging
Adopting eco-friendly packaging presents various challenges that businesses must navigate. This section outlines four primary challenges: cost considerations, performance and durability issues, supply chain adaptations, and consumer acceptance and education.
| Challenge | Description |
| Cost Considerations | Eco-friendly packaging materials often come with higher upfront costs compared to traditional options. Factors such as raw material prices, recycling processing costs, and specialized manufacturing processes contribute to these expenses. |
| Performance and Durability Issues | Some eco-friendly materials may perform better than conventional packaging in terms of durability and protection. Businesses must ensure that sustainable options adequately safeguard products during transit and storage. |
| Supply Chain Adaptations | Transitioning to eco-friendly packaging may require changes in the supply chain, including sourcing new materials and collaborating with suppliers who prioritize sustainability. This can complicate logistics and increase operational costs. |
| Consumer Acceptance and Education | Educating consumers about the benefits of eco-friendly packaging is crucial for acceptance. Many consumers may not understand how to dispose of new materials properly or may be skeptical about their effectiveness compared to traditional options. |
Cost Considerations
One of the most significant barriers to adopting eco-friendly packaging is the cost associated with sustainable materials. While prices have been decreasing as demand increases, eco-friendly options often remain more expensive than traditional materials due to:
- Raw Material Prices: Fluctuations in the cost of bio-based polymers or recycled materials can impact overall pricing.
- Manufacturing Costs: Eco-friendly materials may require specialized production processes that are more costly than conventional methods.
Performance and Durability Issues
Another challenge is ensuring that eco-friendly packaging meets performance standards. Some sustainable materials may not provide the same level of protection as traditional packaging, leading to concerns about product damage during shipping or storage. Companies must:
- Test Materials: Conduct thorough testing to ensure that new packaging solutions meet durability requirements.
- Innovate Designs: Explore innovative designs that enhance the protective qualities of eco-friendly materials without compromising sustainability.
Supply Chain Adaptations
Transitioning to eco-friendly packaging often necessitates changes throughout the supply chain. This includes:
- Sourcing New Materials: Businesses may need suppliers offering sustainable options, which can complicate existing relationships.
- Logistical Adjustments: Implementing new materials might require production processes, transportation methods, and inventory management adjustments.
Consumer Acceptance and Education
Finally, consumer acceptance is critical for the successful implementation of eco-friendly packaging. Many consumers may be unfamiliar with new materials or unsure about their disposal methods. To address this challenge:
- Provide Clear Information: Brands should communicate how to recycle or compost their packaging through labeling or marketing campaigns.
- Educate Consumers: Engage in outreach efforts to inform consumers about the environmental benefits of sustainable packaging and encourage responsible disposal practices.
Government Regulations and Incentives for Eco-Friendly Packaging
Governments worldwide are increasingly recognizing the importance of sustainable packaging. The following section discusses global policies and initiatives, tax incentives and subsidies, and Extended Producer Responsibility (EPR) programs that support eco-friendly packaging practices.
Global Policies and Initiatives
Many countries are implementing regulations aimed at reducing packaging waste and promoting sustainability. Key initiatives include:
- Single-Use Plastics Bans: Numerous jurisdictions have enacted bans on single-use plastics, compelling businesses to seek alternative packaging solutions. For instance, the European Union has set ambitious targets to phase out single-use plastic items by 2021.
- Recycling Targets: Countries like Germany have established stringent recycling targets that require businesses to meet specific recycling rates for their packaging materials. This encourages companies to design more recyclable products.
- Sustainability Standards: Various governments are developing standards for sustainable packaging materials, guiding businesses in selecting eco-friendly options that comply with regulatory requirements.
Tax Incentives and Subsidies
To encourage businesses to adopt sustainable practices, many governments offer financial incentives:
- Tax Breaks: Some regions provide tax deductions or credits for companies that invest in eco-friendly packaging materials or technologies. This can offset the initial costs associated with transitioning to sustainable options.
- Subsidies for Research and Development: Governments may offer grants or subsidies to support innovative sustainable packaging solutions research. This funding can help businesses develop new materials or improve existing ones.
- Support for Recycling Programs: Many local governments provide financial support for recycling initiatives, helping businesses implement effective recycling programs that align with sustainability goals.
Extended Producer Responsibility (EPR) Programs
EPR programs hold producers accountable for the entire lifecycle of their products, including packaging waste. Key aspects include:
- Responsibility for Waste Management: Under EPR regulations, manufacturers must manage the disposal or recycling of their products after consumer use. This incentivizes companies to design more sustainable packaging that is easier to recycle or compost.
- Financial Contributions: Producers may be required to contribute financially to collective waste management systems, supporting recycling efforts and reducing overall environmental impact.
- Transparency Requirements: EPR programs often mandate transparency in reporting the recyclability of packaging materials, encouraging companies to improve their sustainability practices.
Measuring the Impact of Eco-Friendly Packaging
Measuring the impact of eco-friendly packaging involves evaluating its environmental benefits through several key methodologies. This section outlines four primary methods: Life Cycle Assessment (LCA), carbon footprint calculation, waste reduction metrics, and consumer behavior changes.
Life Cycle Assessment (LCA)
Life Cycle Assessment (LCA) is a comprehensive method used to evaluate the environmental impacts of a product throughout its entire life cycle—from raw material extraction to disposal. The LCA process typically involves:
- Goal Definition: Establishing the purpose of the assessment and the scope of the study.
- Inventory Analysis: Collect data on energy use, material inputs, emissions, and waste generated at each stage.
- Impact Assessment: Evaluating the potential environmental impacts based on the inventory data.
- Interpretation: Analyzing results to identify opportunities for improvement and make informed decisions.
Carbon Footprint Calculation
Calculating the carbon footprint of packaging involves measuring the total greenhouse gas emissions associated with its production, transportation, usage, and disposal. This process typically includes:
- Data Collection: Gathering information on energy consumption and emissions from various stages of the packaging life cycle.
- Emission Factors: Applying standardized emission factors to convert activity data into equivalent CO2 emissions.
- Total Emissions Calculation: Summing up emissions from all stages to determine the overall carbon footprint.
Free Eco Tool: Eco-Friendly Packaging Savings Calculator
Eco-Friendly Packaging Savings Calculator
Waste Reduction Metrics
Measuring waste reduction metrics helps businesses assess how effective their eco-friendly packaging strategies are in minimizing waste generation. Key metrics include:
- Waste Diversion Rate: Calculating the percentage of waste diverted from landfills through recycling or composting efforts.
- Material Recovery Rate: Measuring the amount of packaging material recovered for reuse or recycling compared to the total material used.
- Reduction in Single-Use Packaging: Tracking changes in single-use packaging consumption as a result of adopting sustainable alternatives.
Consumer Behavior Changes
Monitoring consumer behavior changes is essential for understanding how eco-friendly packaging influences purchasing decisions and disposal practices. This can involve:
- Surveys and Feedback: Conducting surveys to gather consumer opinions on sustainability and preferences for eco-friendly packaging.
- Sales Data Analysis: Analyzing sales trends before and after implementing eco-friendly packaging to assess its impact on consumer purchasing behavior.
- Social Media Monitoring: Observing social media platforms' discussions and sentiments around sustainable packaging to gauge public perception.
Future Trends in Eco-Friendly Packaging
The landscape of eco-friendly packaging is evolving rapidly, driven by technological advancements and changing consumer preferences. This section discusses four key trends: advancements in eco-friendly packaging materials, integration of smart packaging technologies, closed-loop packaging systems, and packaging-free retail concepts.
Advancements in Eco-Friendly Packaging Materials
The development of new materials is crucial for enhancing the sustainability of packaging. Innovations include:
- Biodegradable Plastics: Bioplastic advances made from renewable resources are becoming more common. These materials can decompose naturally, reducing landfill waste.
- Recycled Content: Manufacturers are increasingly incorporating recycled materials into their packaging. This reduces the need for virgin resources and supports recycling initiatives.
- Innovative Biomaterials: Research is ongoing into materials derived from natural sources such as seaweed, mushrooms, and agricultural waste. These materials offer sustainable alternatives to traditional plastics while being compostable or biodegradable.
Integration of Smart Packaging Technologies
Smart packaging technologies are revolutionizing how products are packaged and delivered. Key features include:
- Embedded Sensors: Technologies like RFID (Radio Frequency Identification) and NFC (Near Field Communication) allow for real-time tracking and monitoring of products throughout the supply chain. This enhances traceability and reduces waste by optimizing inventory management.
- Interactive Features: Smart packaging can provide consumers with valuable information about product freshness and usage through QR codes or digital interfaces. This improves customer engagement and helps reduce food spoilage by providing timely usage information.
- Sustainability Enhancements: Smart packaging can minimize material usage by optimizing designs based on data collected during transit, thus reducing overall environmental impact.
Closed-Loop Packaging Systems
Closed-loop systems aim to create a circular economy for packaging materials. This involves:
- Recycling Initiatives: Companies are increasingly adopting practices that allow for the reuse of packaging materials. For example, brands may implement take-back programs where consumers return used packaging for recycling or refilling.
- Material Recovery Facilities: Investments in facilities specializing in recovering recyclable materials help ensure that packaging is processed efficiently and reused effectively.
- Collaboration Across Industries: Businesses are working to create standardized systems for collecting and recycling specific packaging types, enhancing overall waste management efficiency.
Packaging-Free Retail Concepts
The rise of packaging-free retail is a response to consumer demand for sustainability. Key aspects include:
- Bulk Bins and Refillable Stations: Retailers offer products in bulk bins or refillable containers, allowing customers to bring their containers to shop without generating waste.
- Zero-Waste Stores: The emergence of zero-waste grocery stores encourages consumers to purchase items without any packaging, significantly reducing plastic waste.
- Consumer Engagement: These concepts appeal to environmentally conscious shoppers and foster a sense of community around sustainable practices.
Case Studies: Successful Eco-Friendly Packaging Implementations
Many businesses are embracing the transition to eco-friendly packaging as they recognize the need for sustainable practices. This section highlights notable examples from different sectors that showcase effective eco-friendly packaging solutions.
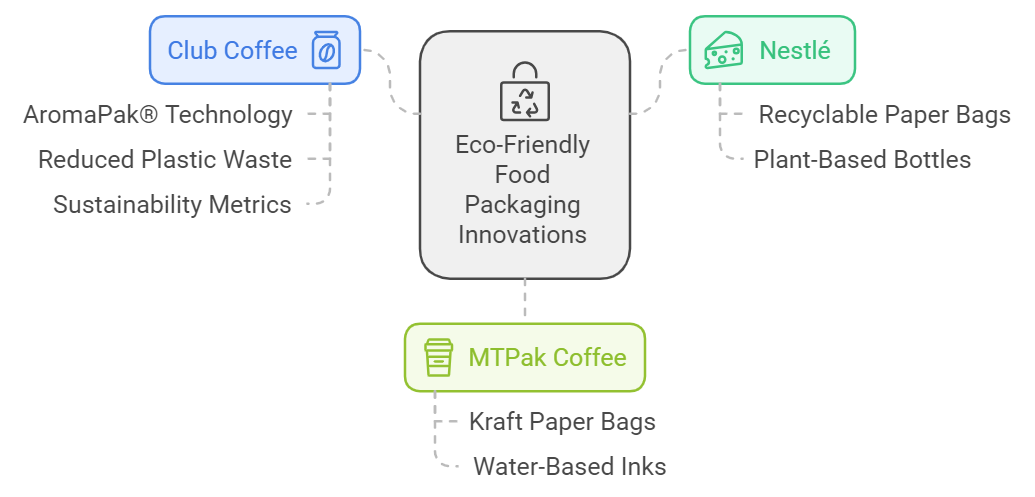
Examples from Leading Brands Using Eco-Friendly Food Packaging
Nestlé has made significant strides in sustainable packaging by making 100% of its packaging recyclable or reusable by 2025. The company has introduced several initiatives, including:
- Recyclable Paper Bags: Nestlé's Nescafé brand has transitioned to using recyclable paper bags for its coffee products, reducing plastic usage and enhancing recyclability.
- Plant-Based Bottles: Nestlé Waters has launched bottles made from 100% recycled plastic (rPET) for its water brands, significantly reducing the carbon footprint of new plastic production.
Innovations in Eco-Friendly Coffee Packaging
Club Coffee has developed AromaPak®, a revolutionary paper fiber-based coffee packaging that uses Boardio® technology. This innovation provides a sustainable alternative to traditional multi-layer plastic packaging. Key features include:
- Reduced Plastic Waste: AromaPak reduces plastic waste by up to 83% compared to traditional canisters and provides a 60% weight reduction compared to metal cans.
- Sustainability Metrics: The lifecycle analysis shows an 86% reduction in CO2 emissions compared to metal cans and a 78% reduction compared to molded plastic canisters, making it a highly sustainable option for coffee packaging.
Small Business Success Stories
MTPak Coffee, a small business specializing in coffee packaging solutions, offers a range of eco-friendly options, including biodegradable and compostable bags made from renewable materials. Their approach includes:
- Kraft Paper Bags: Using unbleached kraft paper that is both biodegradable and recyclable, MTPak Coffee emphasizes sustainability while ensuring product freshness.
- Water-Based Inks: They utilize low-VOC water-based inks for printing, which are safer for the environment and enhance the recyclability of their packaging.
Packaging Innovations That Made a Difference
Frugalpac has developed a fully recyclable coffee cup that addresses the significant waste generated by traditional takeaway cups. Their cup is made from recycled paperboard and features:
- Recyclability: The Frugalpac cup can be recycled in standard paper recycling streams, significantly reducing landfill waste associated with single-use cups.
- Environmental Impact: This innovation aims to eliminate the need for plastic-lined cups that are often non-recyclable, contributing to a more sustainable takeaway culture.
Consumer Guide to Eco-Friendly Packaging
This section offers insights on recognizing eco-friendly packaging, tips for minimizing packaging waste in daily life, and best practices for disposal and recycling.
How to Identify Eco-Friendly Packaging Materials
Identifying eco-friendly packaging materials involves looking for specific characteristics that indicate sustainability. Here are key indicators:
- Recyclable Materials: Look for packaging made from recyclable materials, such as cardboard, paper, glass, and certain plastics. The presence of recycling symbols (like the How2Recycle label) can help consumers understand the packaging's recyclability.
- Biodegradable Options: Packaging labeled as biodegradable is designed to break down naturally over time. Materials like plant-based plastics or paper products often fall into this category.
- Minimalist Design: Eco-friendly packaging often features a minimalist design that uses less material overall. This includes snug-fitting packages that reduce excess space and material usage.
- Sustainable Certifications: Look for certifications from recognized organizations that verify the sustainability of the packaging materials. Certifications like FSC (Forest Stewardship Council) for paper products indicate responsible sourcing.
Tips for Reducing Packaging Waste at Home
Reducing packaging waste at home is an achievable goal with several practical strategies:
- Buy in Bulk: Purchasing items in bulk reduces the amount of individual packaging waste generated. Many stores offer bulk options for food and household items.
- Choose Reusable Containers: Opt for reusable containers instead of single-use plastic bags or wraps. Glass jars, stainless steel containers, and beeswax wraps are great alternatives.
- Avoid Over-Packaged Products: Avoid products with excessive packaging. Select items that use minimal packaging or come in refillable containers.
- Grow Your Own Food: Grow fruits and vegetables at home to avoid any packaging waste associated with store-bought produce.
- Use Natural Cleaning Products: Choose cleaning products that come in recyclable or reusable containers, or make your cleaning solutions using natural ingredients.
Proper Disposal and Recycling Practices
Proper disposal and recycling practices are essential for maximizing the benefits of eco-friendly packaging:
- Clean Before Recycling: Ensure that all recyclable materials are clean and free from food residue before placing them in recycling bins. Contaminated items can disrupt the recycling process.
- Follow Local Guidelines: Familiarize yourself with local recycling guidelines, which vary by region. Check which materials are accepted in your local recycling program.
- Participate in E-Waste Recycling: For electronic products with packaging, participate in e-waste recycling programs to ensure proper disposal of hazardous materials.
- Educate Others: Share information about proper disposal methods with family and friends to encourage collective efforts toward reducing waste.
The Role of Eco-Friendly Packaging in the Circular Economy
Eco-friendly packaging plays a crucial role in advancing the principles of a circular economy by ensuring that materials are reused, recycled, and repurposed effectively. This section covers three key aspects: closing the loop on packaging materials, upcycling and repurposing packaging, and collaborative industry efforts for sustainability.
Closing the Loop on Packaging Materials
Closing the loop on packaging materials means creating a system where used packaging is recycled or reused to produce new products, thereby minimizing waste. Key strategies include:
- Recycling Programs:
Implementing robust recycling programs ensures that materials like plastics, paper, and metals are collected and processed correctly. For example, companies like Unilever aim to make 100% of their plastic packaging reusable, recyclable, or compostable by 2030, keeping materials within the circular economy. - Design for Recycling:
Packaging should be designed with recycling in mind. This includes using single-material solutions that are easier to recycle and avoiding mixed materials that complicate the recycling process. - Closed-Loop Recycling:
This process involves taking used packaging materials and transforming them back into raw materials for new products. For instance, Lacerta is committed to using up to 100% recycled materials in its food packaging by 2025, effectively closing the loop on plastic waste.
Upcycling and Repurposing Packaging
Upcycling involves creatively reusing packaging materials for new purposes rather than discarding them. This practice not only reduces waste but also adds value to discarded items. Examples include:
- Creative Reuse: Consumers can repurpose packaging materials for various uses around the home. For instance, glass jars can be transformed into storage containers or decorative items.
- Innovative Business Practices: Some companies encourage customers to return used packaging for repurposing. For example, brands may offer discounts or incentives for returning empty containers that can be cleaned and reused.
- Community Initiatives: Local organizations often promote upcycling workshops where individuals can learn how to creatively reuse packaging materials creatively, fostering community engagement while reducing waste.
Collaborative Industry Efforts for Sustainability
Collaborative efforts across industries are essential for creating a sustainable circular economy. These initiatives involve partnerships between manufacturers, retailers, consumers, and waste management companies:
- Cross-Industry Collaborations:
Initiatives like the UK Plastics Pact bring together businesses from various sectors to commit to reducing plastic waste through shared goals such as eliminating unnecessary single-use plastics and improving recycling rates. - Research and Development:
Companies invest in research to develop new technologies that enhance recycling processes and create sustainable packaging solutions. For example, Südpack focuses on effective recycling technologies that keep their plastic products within the loop. - Consumer Education:
Educating consumers about sustainable practices is vital for achieving circularity. Brands are increasingly providing information on recycling their packaging correctly and promoting responsible consumer behavior.
Conclusion: The Future of Packaging in a Sustainable World
Innovation in eco-friendly packaging materials is crucial for addressing the growing environmental challenges of traditional packaging methods. The global eco-friendly packaging market is projected to grow from USD 207.86 billion in 2022 to USD 430.38 billion by 2032, highlighting a significant shift towards sustainable practices within the industry.
Continued research and development are essential for creating both biodegradable and recyclable materials and cost-effective and functional. For instance, advancements in biodegradable plastics, recycled content usage, and plant-based materials pave the way for sustainable alternatives that can effectively replace conventional packaging options.
Consumer Demand Driving Industry Change
Consumer preferences are a powerful catalyst for change in the packaging industry. A recent survey indicated that 81% of consumers now demand sustainable packaging, with many willing to pay a premium for eco-friendly products.
This trend reflects a broader societal shift towards environmental consciousness, where consumers prioritize brands that demonstrate a commitment to sustainability. Companies that respond to this demand by adopting eco-friendly packaging enhance their brand image and gain a competitive advantage in an increasingly crowded marketplace.
The willingness of consumers to support businesses that align with their values underscores the necessity for companies to innovate and adapt their packaging strategies accordingly.
The Potential for Global Environmental Impact
The transition to eco-friendly packaging has the potential to significantly improve By reducing reliance on single-use plastics and promoting recycling, biodegradable materials, and minimalistic designs, businesses can contribute to lowering carbon emissions and waste generation.
For example, effective recycling initiatives can divert substantial waste from landfills, while biodegradable options can mitigate pollution associated with traditional plastics. Furthermore, as governments worldwide implement stricter regulations on packaging waste and promote circular economy practices, businesses that embrace sustainable packaging will be better positioned to comply with these evolving standards while contributing positively to global environmental goals.

Leave a Reply